Remote caching and execution
rules_ll uses remote execution compatible toolchains by default, even when you
run local builds.
rules_ll extends Local Remote Execution (LRE)
which disables Bazel's toolchain auto detection and pins every tool to a
reproducible artifact from nixpkgs. This way every system running the same
version of rules_ll uses the same toolchain, regardless of the host's
operating system and locally installed toolchains.
Similar to LRE, the remote execution toolchains in rules_ll achieve virtually
perfect cache hit rates even among different systems sharing the same cache.
Warning
A single compromised machine with write access to a remote cache can easily trigger malicious code execution on all machines reading from that cache.
Local remote cache
If you just want to share build results between different directories on the
same machine, use a local remote cache. Consider using at least this setup
with rules_ll. The initial build of the LLVM project can take a long time
and you probably don't want to rebuild LLVM every time you start a new project.

- Set up a remote cache like NativeLink.
-
Instruct all your local Bazel invocations to use that cache:
~/.bazelrcbuild --remote_cache=grpc://<ip>:<port>
Personal remote cache
If you find yourself running out of disk space, you can move your personal cache to a different machine such as a cloud runner. Since you now access the remote cache via the internet this setup requires some form of authentication:

build --remote_cache=grpcs://<remote_cache>
# Authenticate as instructed by your remote cache provider. For instance
build --remote_header=...
Trusted remote cache
With rules_ll you can share the remote cache among different machines of the
same system architecture and still achieve virtually perfect cache hit rate. You
can set this up like the personal remote cache, just shared by different users:

build --remote_cache=grpcs://<trusted_remote_cache>
# Authenticate as instructed by your remote cache provider.
build --some_authentication_flags
Open remote execution
This setup lets your contributors use cache artifacts from CI runs locally. This way contributors can fetch prebuilt artifacts from upstream without having to rebuild the entire project themselves. This works because the toolchain for local execution reproduces the remote execution environments.
A setup like this lets your contributors use projects the size of LLVM from upstream in 2 minutes from a clean cache on a laptop. They can download prebuilt cache artifacts from the CI pipeline instead of having to rebuild the project themselves.
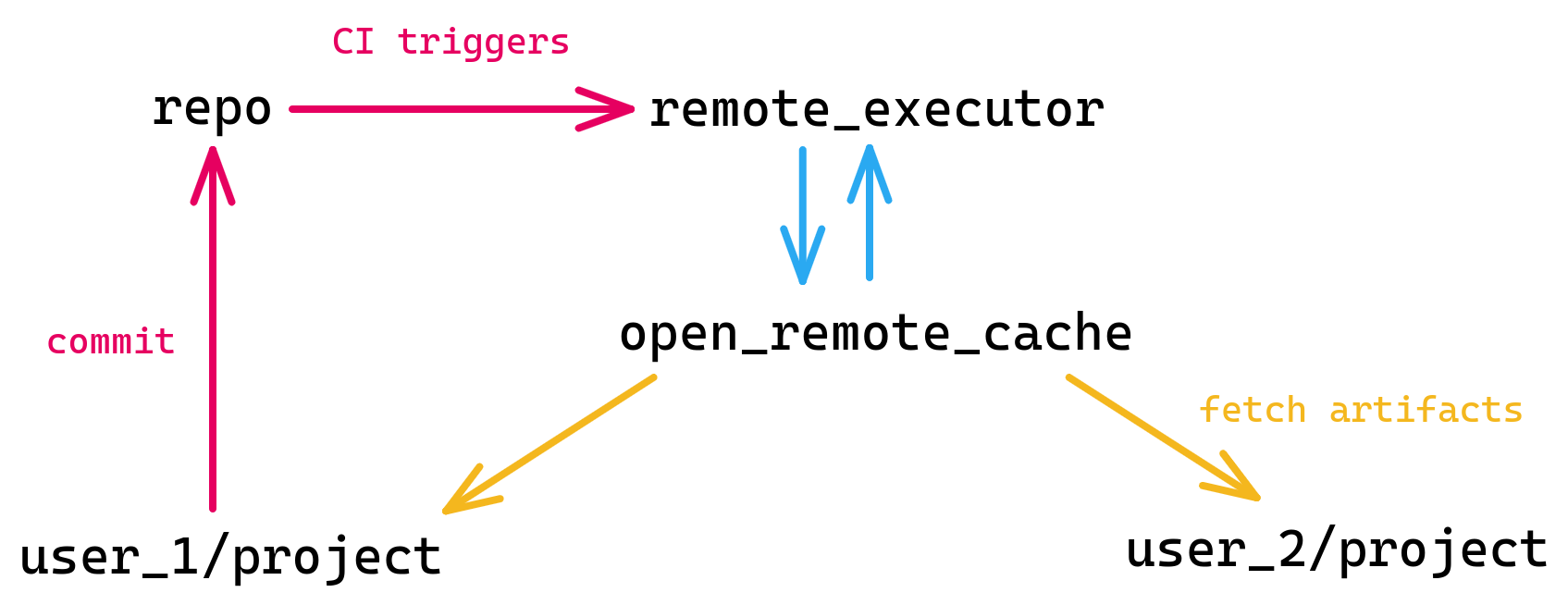
user_1merges a PR.- The CI pipeline triggers the build and tests, using a remote executor.
- The CI runner has write access to the cache so that the remote executor can populate the cache during the build.
- Contributors with read access to the cache can now fetch the latest artifacts as part of their build.
build --remote_cache=grpcs://<open_remote_cache>
build --remote_executor=grpcs://<remote_executor>
build --some_authentication_flag
build --remote_cache=grpcs://<open_remote_cache>
build --some_authentication_flag_only_read_access
build --noremote_upload_local_results